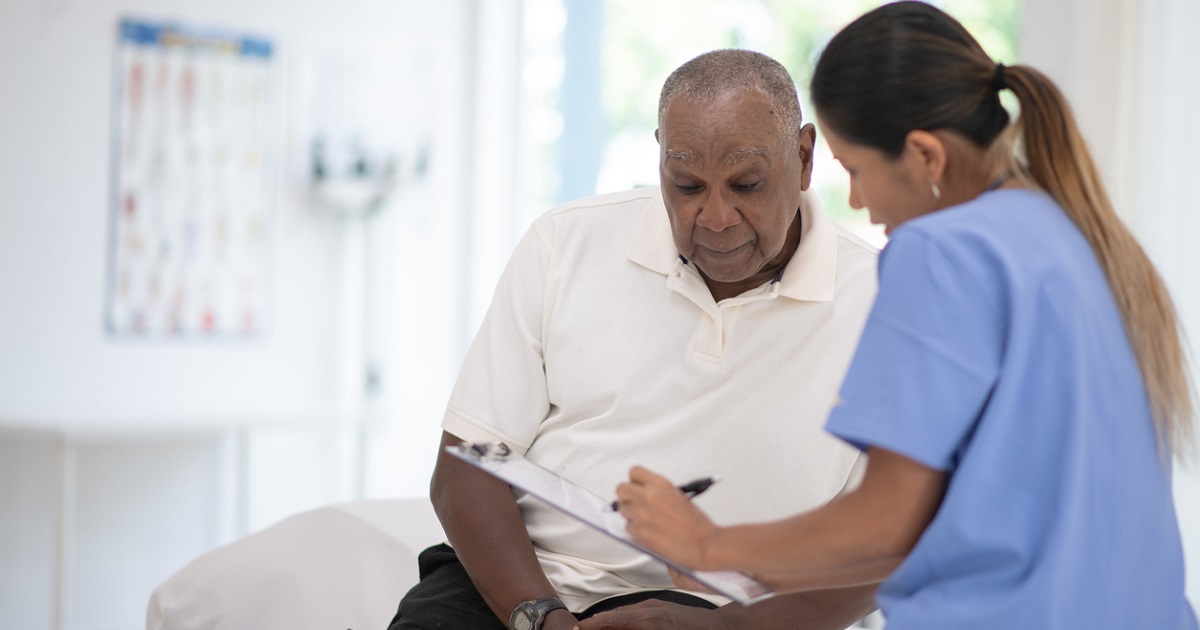
Medical Imaging Locations
Capitol Imaging Services has medical imaging locations across the Southeast United States, including the states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama and Florida. Our growing network of imaging centers continues to grow, providing a wide array of screening and diagnostic testing. Click on any of our medical imaging locations to learn more about services offered, hours of service and general contact information.
is now part of the Capitol Imaging Services family!
Search All CIS Locations
Click Your State or Search By City BelowSelect your state from above or use this search field
Found Locations
View All Locations

M.R. Imaging Systems – Alexandria LA
211 N 3rd St #B
Alexandria LA 71301
Alexandria LA 71301
(318) 443-7674 - Appointment
(318) 443-7696 - Fax
More Info

Open Air MRI of CENLA – Alexandria LA
5413 Jackson Street Ext
Alexandria LA 71303
Alexandria LA 71303
(318) 445-6736 - Appointment
(318) 445-8845 - Fax
More Info

Alliance – Lake Jackson
2760 Brazos Parkway. Suite B&C
Angleton, TX 77515
Angleton, TX 77515
(979) 849-5700 - Appointment
(979) 849-5787 - Fax
More Info

Baton Rouge Imaging Center – Baton Rouge LA
8044 Summa Ave
Baton Rouge LA 70809
Baton Rouge LA 70809
(225) 761-7278 - Appointment
(225) 767-8121 - Fax
More Info

Bluebonnet Imaging Center – Baton Rouge LA
4570 Bluebonnet Blvd #A
Baton Rouge LA 70809
Baton Rouge LA 70809
(225) 298-3223 - Appointment
(225) 298-5474 - Fax
More Info

Central Imaging Center – Baton Rouge LA
11424 Sullivan Rd Bldg B #C
Baton Rouge LA 70818
Baton Rouge LA 70818
(225) 261-7401 - Appointment
(225) 261-3561 - Fax
More Info

PARS Imaging – Baytown TX
1010 W Baker Rd #101
Baytown TX 77521
Baytown TX 77521
(281) 427-5555 - Appointment
(281) 422-7769 - Fax
More Info

Imaging Center of Columbus – Columbus MS
2526 5th St N
Columbus MS 39705
Columbus MS 39705
(662) 328-8402 - Appointment
(662) 328-1554 - Fax
More Info

Radiology & Imaging – Alameda – Corpus Christi, TX
3226 S Alameda St
Corpus Christi, TX 78404
Corpus Christi, TX 78404
(361) 888-8875 - Appointment
(361) 881-6210 - Fax
More Info

Radiology & Imaging – South – Corpus Christi, TX
2825 Spohn South Dr
Corpus Christi, TX 78414
Corpus Christi, TX 78414
(361) 888-8875 - Appointment
(361) 881-6210 - Fax
More Info

Diagnostic Imaging Services – Covington, LA Highway 21
71154 Highway 21
Covington LA 70433
Covington LA 70433
(985) 641-2390 - Appointment
(985) 641-2854 - Fax
More Info

Diagnostic Imaging Services – Covington, LA Pinnacle Parkway
1200 Pinnacle Pkwy #5
Covington LA 70433
Covington LA 70433
(985) 641-2390 - Appointment
(985) 641-2854 - Fax
More Info

Heritage Diagnostic Center – Cullman AL
1705 Main Ave SW #C
Cullman AL 35055
Cullman AL 35055
(256) 734-8175 - Appointment
(256) 734-6296 - Fax
More Info

Open MRI of Mississippi – Flowood MS
2630 Courthouse Cir #A
Flowood MS 39232
Flowood MS 39232
(601) 487-8274 - Appointment
(601) 487-8701 - Fax
More Info

Ascension Open MRI – Gonzales LA
2622 S Ruby Ave
Gonzales LA 70737
Gonzales LA 70737
(225) 450-6125 - Appointment
(225) 450-6327 - Fax
More Info

Open MRI of Hammond – Hammond LA
42078 Veterans Ave #F
Hammond LA 70403
Hammond LA 70403
(985) 340-1960 - Appointment
(985) 340-1967 - Fax
More Info

Homosassa Open MRI – Homosassa FL
8464 W Aquaduct St
Homosassa FL 34448
Homosassa FL 34448
(352) 628-4800 - Appointment
(352) 628-4801 - Fax
More Info

Houston Premier Radiology Center – Houston, TX
12853 Gulf Freeway
Houston, TX 77034
Houston, TX 77034
(281) 464-8200 - Appointment
(281) 464-4343 - Fax
More Info

Alliance – Lake Houston
5514 Atascocita Rd. #180
Humble, TX 77346
Humble, TX 77346
(832) 644-0148 - Appointment
(832) 924-7962 - Fax
More Info

Alliance – Katy
21800 Katy Fwy,
#140
Katy, TX 77449
#140
Katy, TX 77449
(281) 769-8385 - Appointment
(281) 547-7487 - Fax
More Info

Advanced Imaging of Lafayette – Lafayette LA
935 Camellia Blvd #101
Lafayette LA 70508
Lafayette LA 70508
(337) 984-2036 - Appointment
(337) 984-7604 - Fax
More Info

Louisiana PET/CT Imaging of Lake Charles – Lake Charles LA
831 Lakeshore Dr
Lake Charles LA 70601
Lake Charles LA 70601
(337) 433-3001 - Appointment
(337) 433-0540 - Fax
More Info

River Bend Imaging – Laplace LA
490 Belle Terre Blvd
Laplace LA 70068
Laplace LA 70068
(985) 359-7226 - Appointment
(985) 359-0323 - Fax
More Info

Diagnostic Imaging Services – Marrero, LA
925 Avenue C
Marrero LA 70072
Marrero LA 70072
(504) 883-5999 - Appointment
(504) 883-5364 - Fax
More Info

Imaging Center of Meridian – Meridian MS
2021 24th Ave #B
Meridian MS 39301
Meridian MS 39301
(601) 483-4339 - Appointment
(601) 483-4516 - Fax
More Info

Diagnostic Imaging Services – Metairie, LA Houma Boulevard
3434 Houma Blvd #100
Metairie LA 70006
Metairie LA 70006
(504) 883-5999 - Appointment
(504) 883-5364 - Fax
More Info

Diagnostic Imaging Services – Metairie, LA Veterans Boulevard
4241 Veterans Memorial Blvd #100
Metairie LA 70006
Metairie LA 70006
(504) 883-5999 - Appointment
(504) 883-5364 - Fax
More Info

Doctors Imaging – Metairie LA
4204 Teuton St
Metairie, LA 70006
Metairie, LA 70006
(504) 883-8111 - Appointment
(504) 883-3555 - Fax
More Info

Northeast Imaging – Monroe LA
1703 Lamy Ln
Monroe LA 71201
Monroe LA 71201
(318) 570-4985 - Appointment
(318) 450-4040 - Fax
More Info

Alliance – Woodforest
Woodforest Medical Plaza 1
Suite 180
750 Fish Creek Thoroughfare
Montgomery, TX 77316
Suite 180
750 Fish Creek Thoroughfare
Montgomery, TX 77316
(936) 647-2538 - Appointment
(936) 207-1358 - Fax
More Info

Southern Imaging Specialists – Montgomery AL
465 Saint Lukes Dr
Montgomery AL 36117
Montgomery AL 36117
(334) 279-8370 - Appointment
(334) 279-8572 - Fax
More Info

Alliance – Pearland
1910 Country Place Pkwy, Ste 154
Pearland, TX 77584
Pearland, TX 77584
(832) 344-0008 - Appointment
(832) 344-0009 - Fax
More Info

Northwest Imaging – Shreveport LA
1460 E Bert Kouns Industrial Loop #708
Shreveport LA 71105
Shreveport LA 71105
(318) 425-1001 - Appointment
(318) 425-5001 - Fax
More Info

Diagnostic Imaging Services – Slidell, LA
1310 Gause Blvd
Slidell, LA 70458
Slidell, LA 70458
(985) 641-2390 - Appointment
(985) 641-2854 - Fax
More Info

Alliance – Spring
20639 Kuykendahl Rd, Ste 250
Spring, TX 77379
Spring, TX 77379
(832) 610-3305 - Appointment
(832) 514-3647 - Fax
More Info

Texarkana PET/CT imaging Institute – Texarkana TX
1929 Moores Ln
Texarkana TX 75503
Texarkana TX 75503
(903) 794-1994 - Appointment
(903) 794-1996 - Fax
More Info

Alliance – The Woodlands
1011 Medical Plaza Dr, Ste 120,
The Woodlands, TX 77380
The Woodlands, TX 77380
(281) 305-3003 - Appointment
(281) 305-3004 - Fax
More Info

Diagnostic Imaging Services – Thibodaux, LA
2100 Audubon Ave
Thibodaux, LA 70301
Thibodaux, LA 70301
(985) 641-2390 - Appointment
(985) 641-2854 - Fax
More Info

Vestavia Hills Imaging Center – Vestavia Hills AL
2017 Canyon Rd #25
Vestavia Hills AL 35216
Vestavia Hills AL 35216
(205) 824-8262 - Appointment
(205) 824-8264 - Fax
More Info

Alliance – Clear Lake
17490 Hwy 3 Ste. B300
Webster, TX 77598
Webster, TX 77598
(713) 351-4976 - Appointment
(713) 263-3534 - Fax
More Info

Alliance – Montgomery County
9851 FM 1097 Rd West
Willis, TX 77318
Willis, TX 77318
(936) 254-8402 - Appointment
(936) 249-2251 - Fax
More Info




